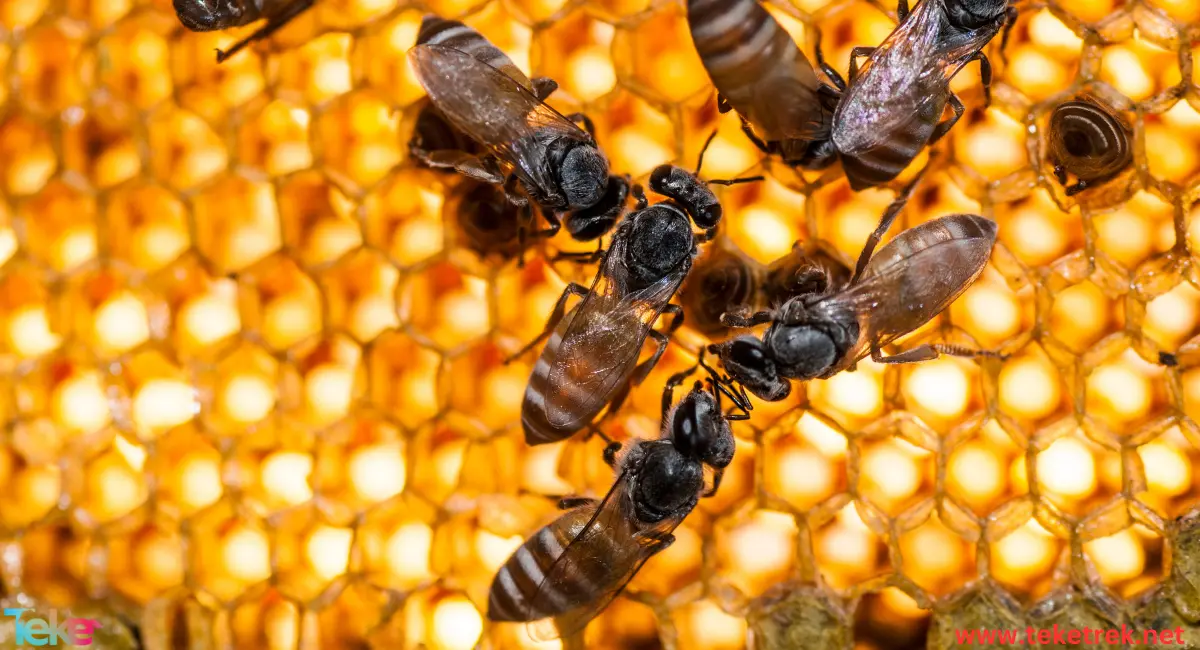
The bee is an intelligent and social creature renowned for its vital role in pollinating plants and producing honey. Its body is composed of a head, thorax, and abdomen, featuring remarkable memory and effective communication through its dances. Bees live in interconnected communities within hives and are characterized by the diversity of their colors. Bees play a crucial role in the ecological cycle and are considered vital partners for humans. In this article from Teketrek we take more about it.

Information Paragraph about bees
- Belonging to the family Apidae, bees are scientifically known as Anthophilia.
- The bee’s body consists of a head, thorax, and abdomen, with four wings and six legs.
- The thorax has three parts, each carrying a pair of strong legs and a pair of delicate wings on the rear segments.
- The abdomen has nine parts, with the third part transforming into a stinger. This means that the third part of the abdomen differs in structure and function to serve as a specialized defense and stinging mechanism in females.
- Bee sizes vary from small, stingless bee species with worker lengths less than 2 millimeters to large honeybees, the largest bee species, with female lengths reaching up to 39 millimeters.
- Bees display a diverse range of colors, including brown, black, and orange. Colors change with the seasons.
- Bees are characterized by their long antennae used for sensing scents and locating nectar and flowers. The antennae play a vital role in guiding bees to food sources and assessing nectar quality.
- Mouthparts are adapted for chewing and sucking, featuring a pair of mandibles and a long proboscis for nectar absorption.
- Sensory antennae in bees typically consist of 13 segments in males and 12 in females, resembling articulated appendages extending at their midsection. These antennae carry sensory organs capable of detecting touch, smell, and taste, along with small hair-like sensors for detecting air movement to hear sounds.
- Bee heads have complex eyes called compound eyes covering most of the head’s surface. Three small eyes are located between and above them, allowing bees to see objects well even in changing light conditions. Eyes assist in guiding bees during flight and searching for food sources.
Characteristics of the bee
- Bees have four wings that aid in flying and transferring pollen between flowers. The wings are covered with a thin layer of wax, enabling bees to fly and collect nectar from flowers.
- Bees move at a speed ranging from 24 to 28 kilometers per hour.
- Bees differ from related groups like wasps in several features, including the presence of secondary or feather-like hair, a brush on the front edges to clean sensory devices, minor differences in appendage structure, and venation patterns in the hind wings. In females, there is a division of the seventh dorsal plate into two parts.
- There are several species of bees, each with its unique characteristics.
The wonders of bees
1. Bees use complex dances inside the hive to guide their fellow bees to food sources. This dance is an effective way to transfer information within the colony.
2. Bees collaborate in collecting nectar and converting it into honey in wax cells inside the hive, it is a goof nutrition source.
3. Bees play a crucial role in pollinating plants, leading to increased fruit production and enhancing biodiversity.
4. Bees possess an incredible memory, being able to remember food locations and efficiently return to them.
5. Bee colonies are managed in an organized and social manner, where each bee has a specific role and importance in the social system.
6. Bee honey is considered a natural antiseptic due to its germ-fighting properties, making it effective in treating some infections.
7. Bees can determine the queen’s gender based on the type of food the larvae receive, reflecting remarkable genetic control.
8. Bees are known for their generosity, as many worker bees produce a massive amount of honey in their lifetime, providing significant energy for the community.
9. The organization and balance of the bee colony system throughout its life cycle between worker bees, queens, and males are among the most astonishing phenomena in the creature world.
10. One of the wonders of bees is the phenomenon of intoxication, where some bees consume substances like ethanol while collecting nectar. The effect of these substances changes the bee’s behavior, making it aggressive and harmful. The impact lasts up to 48 hours.
11. Intoxicated bees can lead to the contamination and poisoning of honey.
Home defense
- Bees unite to defend the colony collectively when there is a threat, with honeybees considered one of the most defensive animals.
- Guard bees monitor and expel intoxicated bees from the hive, and upon their return after sobering up, they break their legs to prevent them from repeating substance abuse.
- Bees can fly extremely long distances and at high speeds, making them one of the fastest insects in our natural world.
Cellular engineering in the construction of bee hives
The bee exhibits astonishing engineering skills in building its cells, characterized by precision and efficiency. Here are some aspects of cellular engineering:
1. Hexagonal Geometry:
- Bee cells are constructed in a hexagonal shape, featuring precise geometric organization. The cells are angled meticulously to reduce wax consumption and achieve optimal space economy.
2. Natural Cooling:
- Cells are arranged to allow air flow between them, working to cool the hive in summer and warm it in winter.
3. Smart Wax Usage:
- Bees use wax efficiently in cell construction, producing it from glands in their bodies and reusing it several times to reduce building effort.
4. Digestive Resistance:
- Cells are designed to be resistant to digestion and corrosion, ensuring their durability over an extended period and maintaining the hive’s environmental integrity.
Bee habitat and locations
- The bee lives in its communities known as hives. Bees are found in various environmental regions, ranging from meadows and forests to urban areas.
Bees are distributed on every continent except Antarctica. They are present in:
- Europe: Playing a vital role in plant pollination and honey production.
- North America: Found in Canadian regions to Mexican deserts.
- Africa: Exists in savannas and the vast deserts.
- Asia: Spread throughout the continent from dense forests to meadows.
- South America: Present in urban, rural, and tropical forest areas.
- Australia: Plays a role in the pollination of wild plants and the cultivation of fruits and vegetables.
Reproduction in the world of bees
The bee animal is non mammal animal, it relies on a complex and organized reproductive process that contributes to the colony’s continuity. Here’s an overview of the bee’s reproductive process:
1. Sexual Reproduction:
- The reproduction process begins with the queen mating with males outside the colony. The queen takes flight, and males compete to mate with her.
- Males typically seek females for mating. After mating, the female stores the sperm and determines the egg’s gender during laying. Fertilized eggs produce males, while unfertilized eggs produce females.
2. Pollen Collection:
- After mating, the queen collects pollen transferred from males to the pollen sacs in her body. This pollen plays a crucial role in the subsequent pollination of flowers.
3. Pollen Storage:
- The queen stores the collected pollen in a special pocket in her body, using it as needed throughout her life.
4. Egg Laying:
- The queen lays large quantities of eggs to ensure the colony’s continuity. A queen bee can lay eggs daily, reaching thousands per day inside the hive. The eggs exit her ovipositor and are fertilized by the stored sperm.
5. Larval Development:
- The egg’s incubation period is short, typically ranging from 3 to 5 days. Upon hatching, a small larva appears, developing over time into a worker bee, a queen bee, or a drone based on the colony’s conditions and needs.
6. Task Allocation:
- Worker bees perform specific tasks within the colony, while the queen’s role involves laying eggs and guiding the colony’s path.
7. Cycle Renewal:
- This recurring process continues to ensure the colony’s sustainability, bee reproduction, and the development of different generations.
Human uses of bees
The bee provides numerous important benefits and human uses, including the production of honey, beeswax, and pollination of plants.
The difference between males and females in the bee community
1. Primary Roles:
- Females (Worker Bees): Carry out most tasks within the colony, such as collecting nectar and pollen, caring for larvae, and building wax combs.
- Males (Drones): Play a crucial role in mating with queens outside the colony.
2. Body Structure:
- Females: Have a robust body and shorter wings, making worker bees easily distinguishable.
- Males: Feature longer wings and a slimmer body, often being larger than worker bees.
3. Age and Lifespan:
- Females: Have a shorter lifespan in the summer and a longer one in the winter.
- Males: Live for a short period after mating and often die afterward.
4. Stinging:
- Females: Worker bee stings can be painful, but they typically leave no swelling, unlike a queen bee sting.
- Males: Lack stingers, so they cannot sting.
5. Number of Wings:
- Females: Have two pairs of wings.
- Males: Possess four wings, with two on each side.
Bee food
The food of bees consists of several nutritional elements that meet their vital needs. Here is an overview of the components of bee food:
- Honey: Produced from the nectar of various flowers, honey is a primary food for bees. It contains sugars, vitamins, minerals, and antibiotics.
- Pollen Grains: Pollen grains are a crucial part of bee food, containing proteins, vitamins, minerals, and essential amino acids.
- Nectar: Bees collect flower nectar, a source of energy containing sugars and flavors, which is used in honey production.
- Water: Bees need water to cool the hive and regulate temperature, especially in the summer.
- Larval Food: Larvae feed on pollen, a rich source of protein, minerals, and vitamins that contribute to their growth and development.
- Royal Jelly: Specially prepared for the queen, royal jelly includes honey and pollen, making it rich in nutritional elements.
Medical uses of bees
The bee and its products have various medical uses, considered part of folk medicine and complementary medicine. Here are some well-known medical uses:
1. Honey Usage:
- People use honey as a natural antiseptic for wounds and burns.
- It can act as a soothing remedy for coughs and sore throats, being a natural antibiotic.
2. Bee Stings:
- Some people consider bee stings a treatment for joint pain and rheumatism, believing that bee venom stimulates blood circulation and reduces pain.
3. Pollen Products (Propolis):
- Promoters advocate the use of pollen products to boost the immune system and enhance overall health.
4. Beeswax Products:
- The cosmetics and skincare industry utilizes beeswax.
5. Royal Jelly:
- People consider royal jelly a rich source of nutrients and may use it as a dietary supplement.
The best Types of bees
There are various types of bees, and the preferred species depend on the needs and purposes of beekeeping. Among the common and important species are:
1. Honey Bee (Apis Mellifera): This is the most famous and widespread bee species used in beekeeping for honey production.
2. Mason Bee (Osmia spp): Used in pollinating certain plants, particularly effective in fruit and vegetable cultivation.
3. Carpenter Bee (Xylocopa spp): Excavates holes in wood and contributes to pollinating flowers.
4. Sweat Bee (Halictidae): A small, socially living bee considered effective in pollinating plants.
5. Long-tongued Bee (Megachile spp): Known for constructing random nests, used in pollinating a wide range of plants.
6. Yemeni Honey Bee (Apis mellifera jemenitica): A bee species found in Arab regions, especially in Yemen, characterizes itself with brown color and transparent wings. It plays a crucial role in pollination and forms small colonies in various environmental areas.
In addition to that, there are Stingless bees, Drones bees, Bumble bees.
The best Species of honey
- One of the best Speciesof honey is pure Sidr honey, extracted from the nectar of Sidr tree flowers. Its rich and luxurious taste, often accompanied by a dark color and a heavy texture, distinguishes this honey. Pure Sidr honey is particularly sought after for its unique and distinctive flavor.


FAQ
- Why is bees important?
Bees are important because they play a crucial role in pollinating plants, which is essential for the production of fruits, vegetables, and seeds. Without bees, many plants would not be able to reproduce and the food chain would be greatly disrupted.
- What does a bee eat?
Bees eat a nectar, where the sugary liquid is produced by the flowers. They also collect pollen, which is a source of protein for them.
- What do bees do all day?
Bees are very busy creatures and spend most of their day collecting nectar and pollen from flowers to bring back to their hive. They also maintain and build their hive, care for the queen bee, and take care of the eggs and larvae.
- Do bees drink water?
Yes, bees do drink water. They need water to dilute the honey they eat, regulate the temperature in their hive, and cool down on hot days. Bees typically collect water from sources like puddles.
- What are the benefits in human life?
Producing honey, which contains many benefits and benefits of plants, which helps in increasing agricultural production also of the wax that bees produce in cosmetic products.
- Does he see or not?
They do not have the ability to see things as comprehensively as humans, but rely mainly on the sense of smell and touch for orientation and climbing.
- How long does a baby sleep?
The duration of nesting varies depending on the bee species and environmental conditions, and can range from 4 to 14 hours per day.
Finally
The bee appears not just as an insect but as a vital partner in the environment and human life. By understanding its characteristics and behavior, we realize the importance of preserving this remarkable creature to ensure the balance of the ecosystem and the sustainability of life.