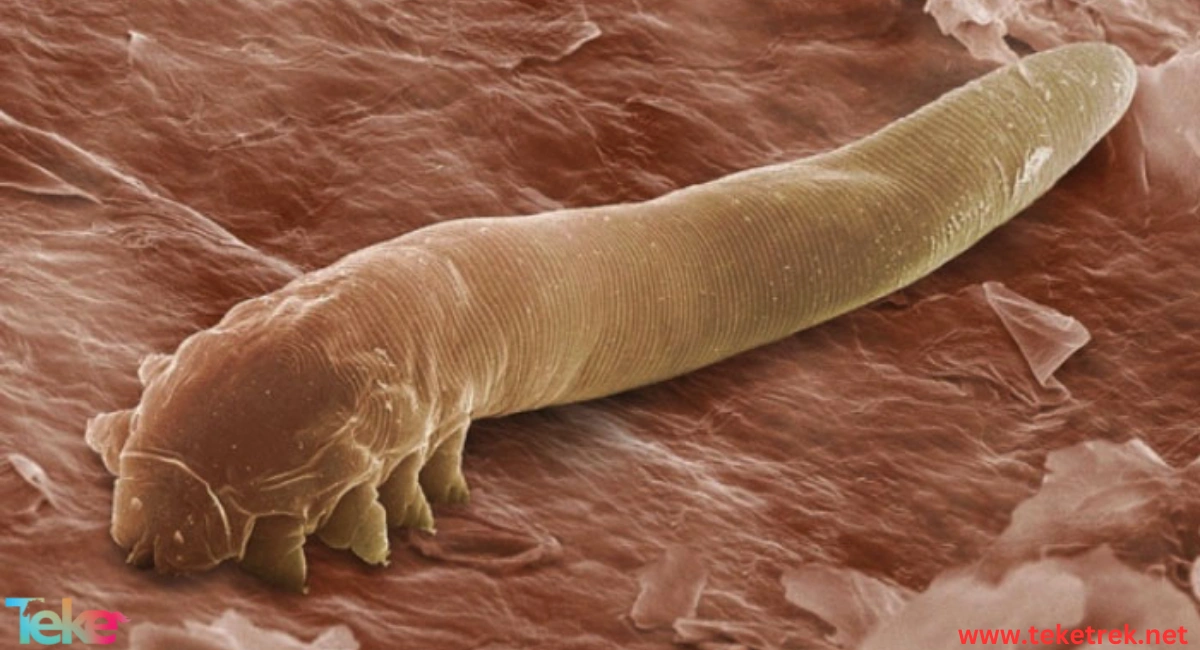
Flatworms are one of the parasitic organisms. Below on the teketrek website, we talk more about them, their characteristics, classifications, habitats, and how they reproduce.
Now let me tell you what some facts about flatworms are.
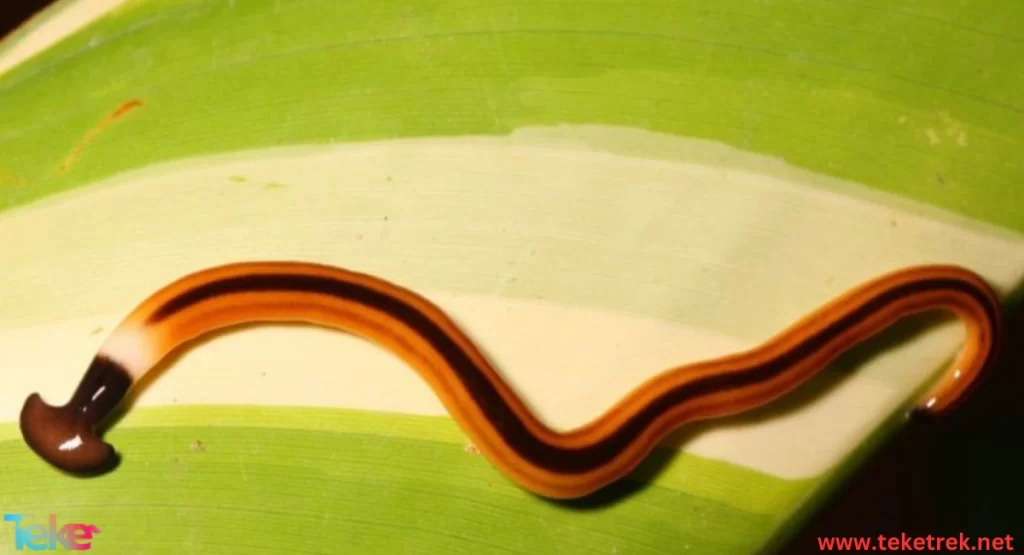

An introduction to flatworms
Flatworms, or as they are called broadworms or broadworms in English, Platyhelminth, are the simplest forms of worms, from the phylum Flatworms in the classification of animals that includes soft invertebrates.
- Its body is bilaterally symmetrical and its center is flat. It resembles a ribbon. It contains about twenty thousand species.
- Each of them has its own behaviors. Some live freely, while others parasitize on another organism and take its food from it.
- It lives in both seawater and pure water. It is considered a tapeworm.
- Flatworm reproduces through division, where it divides into two parts, and a new flatworm is formed as a result.
Characteristics of flatworms
The right and left parts of the worms’ bodies are similar, as they are characterized by symmetry or bilateral symmetry.
It has a body so thin that it can be seen through a microscope, and it reaches several feet in length.
Body structure of flatworms
The body of flatworms consists of three layers of cells:
- Ectoderm is the outer covering.
- Endoderm lining the sites of digestion, almost like cnidarians.
- Mesoderm is located between the extrinsic and endoderm layers.
Tapeworms do not have a digestive system like adults, but their surfaces are similar in structure to the cells lining the intestines.
Their bodies also contain 3 layers of tissue with organs and organelles, and they lack internal cavities, as they do not contain a dedicated skeletal, circulatory, and respiratory system:
Digestive system in flatworms
- It contains blind intestines, as it has a mouth without an opening at the lower end of the digestive canal. It also has protonated excretory organs instead of the opening designated for removing waste from the body.
- It has a combination of digestive and excretory systems, as it obtains food and expels waste through the same opening.
- It also has branched intestines that help it transport food to all parts of the body.
How do flatworms feed?
- Flatworms are carnivores that use their proboscis to obtain food from dead or injured animals and colonial animals, including corals, prions, insects, and microscopic organisms.
How do flatworms breathe?
- Flatworms do not have lungs or even a respiratory system. Rather, they breathe by absorbing oxygen directly through the skin and delivering it to internal cells.
- This process is called cutaneous respiration.
Skeletal system
- Flatworms are characterized by not having a skeleton or muscles either, but they can move or slide quickly on their abdomen using fine hair-like cilia that cover their body in addition to the presence of two layers of muscles under their skin, and these worms can swim for a good period of time in the form of waves.
Nervous system
- The nervous system of flatworms is very simple, as they have two nerve endings at each end, and they also have two simple brains called ganglia, which are made up of a group of nerves. In addition, they have eyes that make them sense light.

Classification of flatworms
Flatworms are a group of multicellular eukaryotic organisms called isopods, belonging to the branch of Ekarya, and consisting of three subgroups:
Turbellaria
- It is considered the only living, non-parasitic species that you will find roaming in the natural environment, and inhabiting aquatic environments such as fresh water, oceans, and wet terrestrial habitats. It crawls around the lower surfaces of most objects in the water. It consists of several subspecies that are divided according to the structure of the digestive cavities, the most prominent of which are Dugesia worms and flatworms.
Trematodes
- Flukes are called worms, and they are parasites that feed on the host, whether it is a human or a pet. Their life cycle is complex, dedicated to parasitizing on animal tissues. They are classified into several types according to the host organ in which they have made their home. Flukes include the liver, intestines, blood, or lungs. These types include:
- Schistosoma is a blood fluke, lateral paroxysmal Westerman, lung fluke. Clonorchis sinensis, or Chinese liver fluke.
- Tapeworms, which are tapeworms or logicians.
Sizes of flatworms
The size of flatworms varies depending on their type:
- Turbularia:
They are characterized by their microscopic size, most of which do not exceed 5 mm in length. Planarian worms are considered the largest worms in size, as they are
Its length reaches half a meter. Flukes:
Most of them range from 1 to 10 mm in length, sometimes several centimeters.
- Regions:
Some can reach 15 m in length, with the smallest being only 1 mm long.
Monogenea ranges in length from 0.5 mm to 30 mm.
The length of the abdominal carapace ranges from several millimeters to 100 mm.
Reproduction in flatworms
The life cycle of flatworms is fairly simple, and is manifested in the following steps:
- Fertilized eggs are laid collectively or singly, and are attached to a surface through an adhesive secretory substance.
- Then tiny larvae or worms emerge from them that can swim after the embryonic development stage ends.
- It goes through several stages and then develops into adult worms that complete its life cycle.
- In general, flatworms are hermaphrodites, as each individual has male and female reproductive organs, and thus the organism produces eggs and sperm at the same time.
Where do flatworms live?
Most flatworm species are parasitic, so trematodes and cnidarians live on the bodies of vertebrate hosts. Tapeworms live in the host’s digestive system, while flukes live in the host’s circulatory system or liver.
FAQ
One of the most frequently asked questions about Flatworms:
- What are the types of flatworms?
Turbellaria, flukes.
- Why are flatworms given this name?
Because it has a bilaterally symmetrical body and a flat center.
- What are the characteristics of flatworms?
The right and left parts of its body are similar, it has a thin body, and reaches several feet in length.
- How is food distributed and absorbed in flatworms?
Through the process of diffusion.
- How do you identify a flatworm?
Ribbon-like, with a bilaterally symmetrical body and a flattened center.
In short, flatworms are considered one of the vertebrate organisms that parasitize the body of other organisms. They have several types that differ from each other in terms of size.